Description
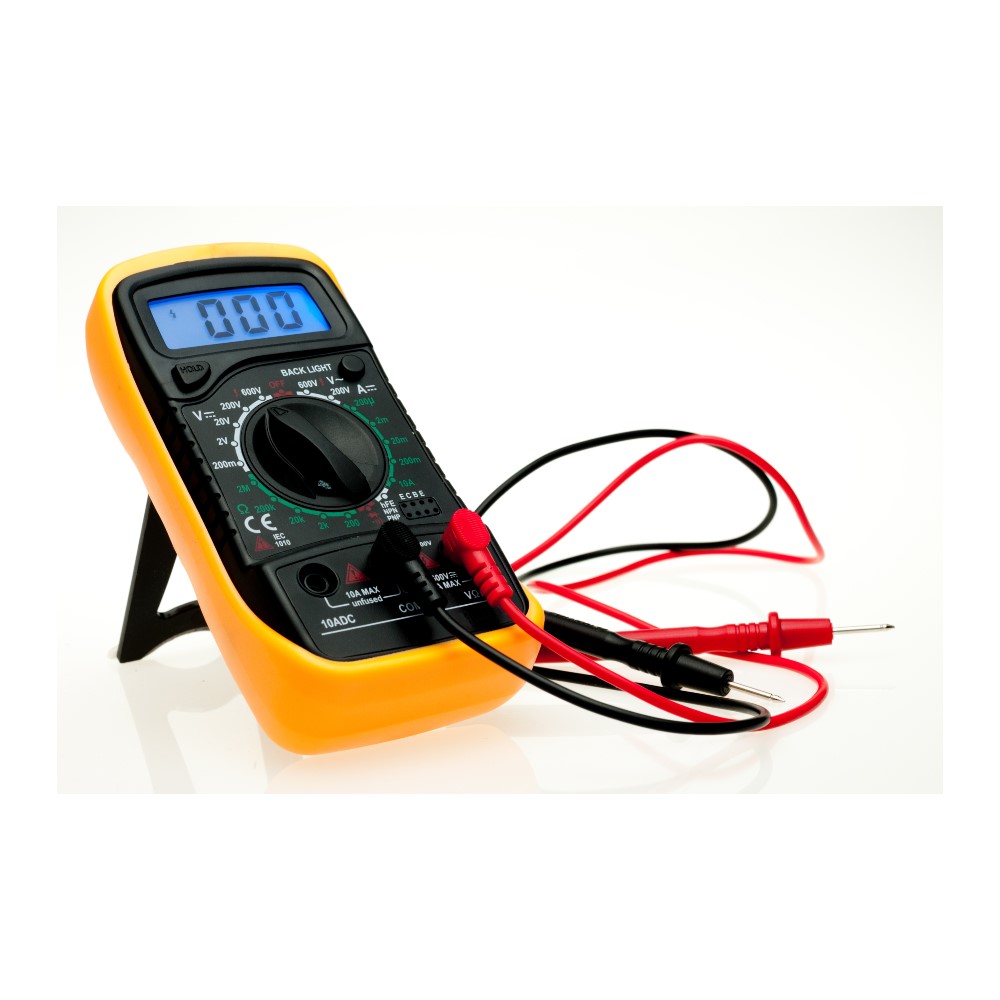
A digital multimeter (DMM) is a device that provides multiple types of measurements within one device. DMMs use a more accurate and readable digital output than an analog solution. Without using a Digital Multimeter to immediately measure live voltage and currents, there is a risk of painful shocks that can even be lethal. Therefore, it poses a serious safety hazard.
Modern multimeters are often digital due to their accuracy, durability, and extra features. In a digital multimeter, the signal under test is converted to a voltage, and an amplifier with electronically controlled gain preconditions the signal. A digital multimeter displays the quantity measured as a number, which eliminates parallax errors.
Modern digital multimeters may have an embedded computer, which provides a wealth of convenience features. Measurement enhancements available include:
- Auto-ranging
- Auto polarity
- Sample and Hold
- Current-limited tests for the voltage drop across semiconductor junctions.
- A graphic representation of the quantity under test, as a bar graph
- A low-bandwidth oscilloscope.
- Automotive circuit testers, including tests for automotive timing and dwell signals
- Simple data acquisition features to record maximum and minimum readings over a given period or to take a number of samples at fixed intervals.
- Integration with tweezers for surface-mount technology
- A combined LCR meter for small-size SMD and through-hole components